Automated analysis of pottery by QEM-EDS
A case study from Mansiri, Sulawesi
https://doi.org/10.34780/b92n-4tna
Abstract
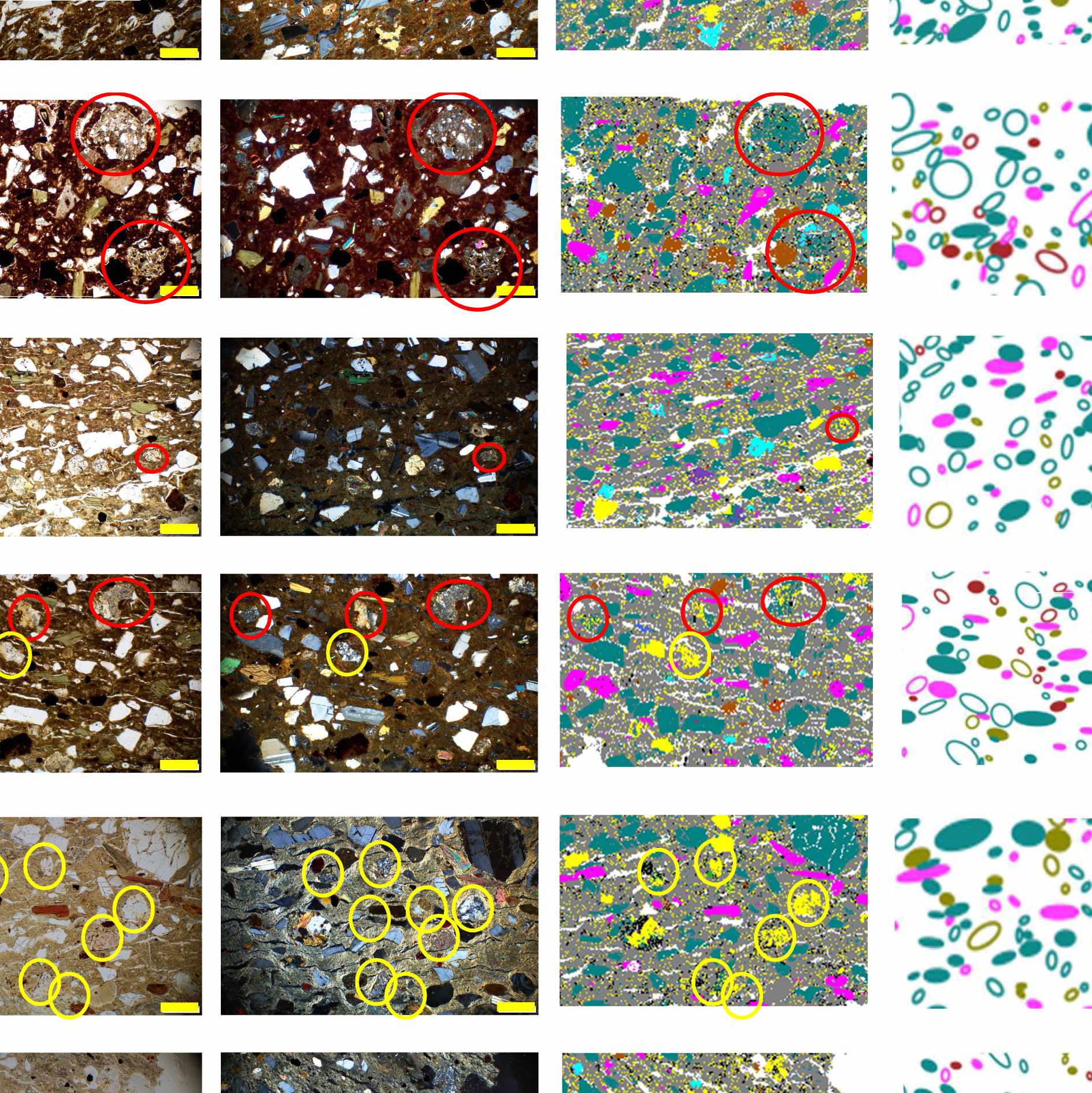
The analysis of raw materials and manufacturing techniques is central to the investigation of pottery assemblages. While various analytical techniques exists, petrography generally remains the go-to method to analyse the fabric of pottery. It combines relatively cheap and simple sample preparation protocol with the ability to yield very detailed information related to provenance and manufacturing technique. Here, we test the utility of performing QEM-EDS on archaeological pottery from the Mansiri site, Sulawesi, to complement petrographic observations. We identify the main non-plastic inclusions as plagioclase, quartz, calcic amphibole, iron oxides and volcanic rock fragments, consistent with the pottery being made locally. Quantitative analysis of inclusion size and direction suggests that the non-plastic inclusions were not manually added, and that in contrast to other Neolithic Sulawesi sites, coiling with beating/paddle and anvil was used to manufacture the pots.
Schlagwörter:
Island Southeast Asia , Sulawesi, Quantitative Mineral Analysis, QEMSCAN, automated petrographic analysis, Pottery